There are many RAID setups to choose from, one of the more popular ones is Raid 0 vs Raid 1. Raid 0 is often considered the better option for most users, due to its cost-saving and performance benefits.
Raid 1 is similar to Raid 0, but it also offers data redundancy in case one of the drives in the array fails, which is a significant factor for many business users. Read on our guide to help you decide if a RAID 0 or RAID 1 array is right for you.
What is RAID 0?
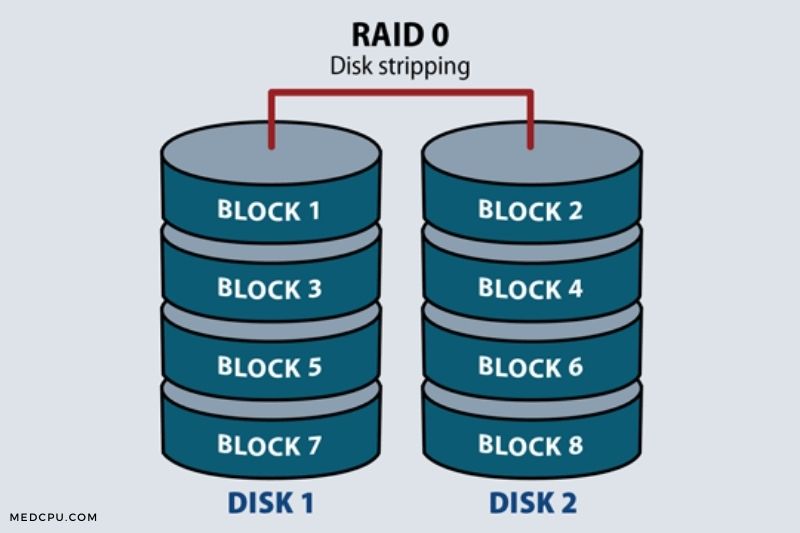
RAID 0 is also known as a striped volume, dynamic volume. To create RAID 0, you will need 2 or more hard drives. RAID 0 has the greatest merit of improving the performance and throughput on a hard drive.
The biggest drawback is that RAID 0 does not provide fault tolerance or parity information redundancy. This means that you’ll lose all data on the array if any disk fails and that the entire system will be affected. RAID 0 is not recommended for critical systems.
A striped array is possible if there is enough disk space to be added by each disk to the array.
Advantages:
- RAID 0 delivers outstanding performance in both read and write operations. Parity controls do not cause overhead.
- Four drives can be striped to provide four times the bandwidth. This improves performance. This setup will be super fast for users if each drive runs at approximately 250 Input Operations per Second (IOPS).
- No overhead: RAID 0 does not use parity, and all of the drive’s storage capacity is used for storing.
- This configuration is the most affordable of all RAID levels, and all RAID controllers support it.
- It’s easy to implement: RAID0 is very simple to set up, and it’s also the easiest and fastest to implement.
Disadvantages:
- It is impossible to recover lost or corrupted data if RAID 0 is no parity. RAID 0 is not suitable for critical data.
What is RAID 1?
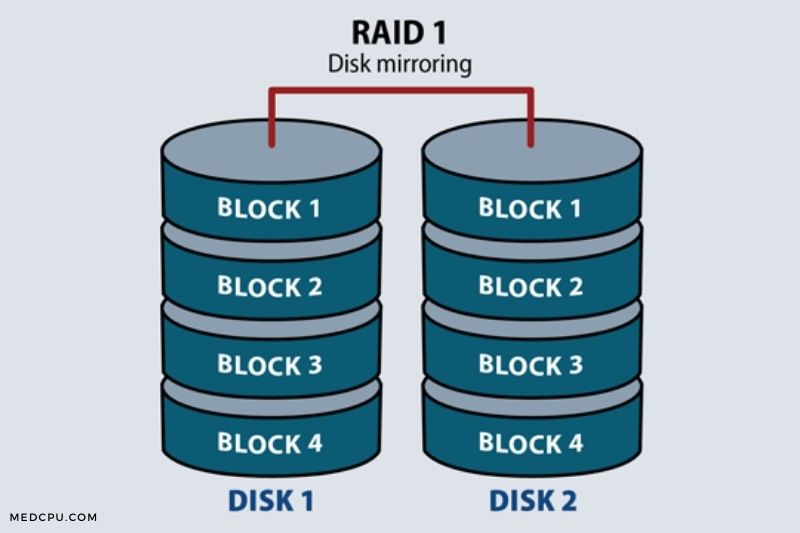
RAID 1 can also be known as a mirror volume, which requires at least 2 disks. It stores a copy of all data on the disks. This configuration provides high data security due to its fault tolerance and redundancy. This means that you can still restore the original data using the mirrored drive.
When creating it, you must ensure that the RAID 1 array is at least twice the size of the smallest disk. This array will still function normally as long as one of its disks is available. However, it is important to promptly replace the failing hard drive in the event of an operating system crash.
Advantages:
- Data redundancy: RAID 1 has the most significant advantage because data is replicated on multiple disks.
- Fault tolerance: This level of tolerance is best for mission-critical applications. The other drive will automatically take over if one fails. Users will not be affected because both drives have identical data.
- High availability: Data is replicated across multiple drives, so it is always available. There is also no chance of data loss.
- High performance: Data can easily be read from multiple devices simultaneously.
Disadvantages:
- Storage capacity reduced: Because the same data must be stored twice, your storage capacity is only half.
- Real-time swapping is not possible: The secondary disk does not take over when a disk goes out. This can cause some inconvenience as the system must be restarted before it takes over.
- Expensive: RAID 1 requires more space, making it more costly than RAID 0.
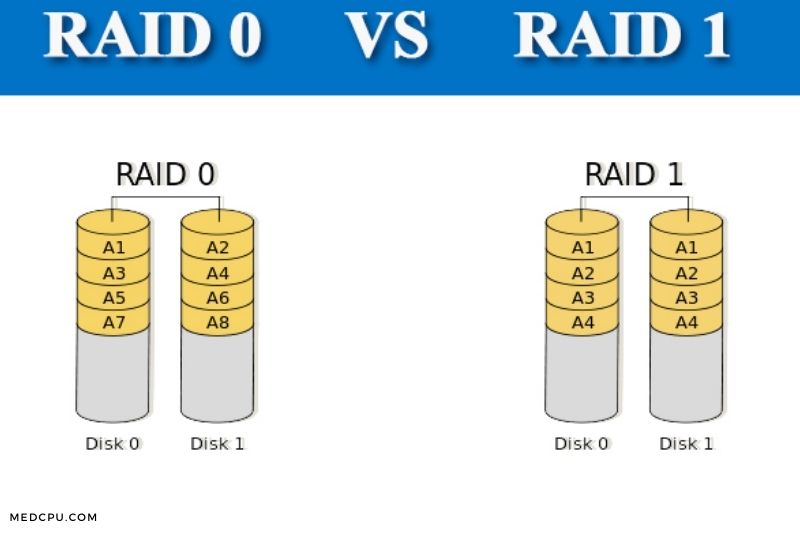
RAID 0 Vs RAID 1
Comparison Chart
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | RAID 0 | RAID 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Striped array with no fault tolerance | Disk mirroring |
| Cost | Inexpensive | Expensive comparatively |
| Relative storage efficiency (in %) | 100% | 50% |
| Read performance | Perform well in both random and sequential reads. | Moderate but better than a single disk. |
| Write performance | Better than RAID 1. | Slower than a single disk. |
| Write penalty | No | Moderate |
| Appropriate | When the data accessing speed is the main concern. | When the emphasis is on Data availability. |
Performance
Writers
RAID 0 allows for speedy write times as the data is split up and written to multiple disks simultaneously. RAID 1 writes slower than RAID 0, but they are about the same speed as writing to a single drive. The entire data is written to two separate disks simultaneously.
Reads
RAID 0, however, also allows for quick reads. In ideal situations, the array’s transfer speed is equal to the sum of all disks. This speed is limited only by RAID controller speed. Depending on the RAID controller, reads from RAID 1 might offer a performance boost.
Smart controllers divide the reading task so that data redundancy is taken advantage of and different blocks are read from different disks. This provides a performance boost similar RAID 0, but controllers are not capable. Read speeds are approximately the same as a single drive.
Applications
RAID 1 is better if reliability is an issue and data loss is not an option. Data archival requirements are a typical example. RAID 0 is a better option in situations where a large amount of high-speed storage will be required.
A large hard drive is required to store uncompressed HD video on HDSDI. Large databases with logs and other information that have a high number of reading operations are another example.
Storage Capacity
RAID 0 has a greater storage capacity than RAID 1. RAID 0 has no redundancy, so the maximum storage you can use is the sum of all disk storage capacities. In a RAID 1 array, however, the total storage is equal to one hard disk.
You have two hard disks with 500GB each. This meant that a RAID 0 device’s total storage capacity is 1000GB. A RAID 0 device has 500GB.
Configuration
It would be helpful to show a diagrammatical explanation of RAID 10 or RAID 01 to understand the configurations better. This will help you understand how RAID 10 or RAID 01 have changed the definition of data storage strategies.
RAID 10, also known by RAID 1+0, is the theoretical name for a Stripe of Mirrors. This configuration works well on at least four disks. Each disk is paired in two for mirroring. This is evident because RAID 10 would only have three groups if there were less than 6 disks.
If a group contains Disk 1 or Disk 2, the data on both disks are mirrored. This means that data across Disk 1 will be the same as Disk 2. However, the groups are striped.
It is a nested RAID 01 configuration of RAID 0,+1. This configuration has been recalled as the Mirror of Stripes. It can be used on three disks, but it’s most effective when implemented on four. This is why you should consider six disks, which are arranged in two groups each of three disks.
Each group has its data striped. Every block is associated with an individual disk. The data across each group is mirrored on the disk with the same block as the first group. It is also known as a mirror of stripes in theory.
Read/Write
RAID 0 allows for very fast read and write speeds, as the data is split among two or more drives. RAID controller speed is only a limitation. Normally, the transfer speed for an array is equal to the transfer speed for all disks.
RAID 1 is slower than RAID 0, but it writes to a single drive at the same speed. RAID 1 is slower than RAID 0, but it can write everything twice if you have two drives. RAID 1 is faster in terms of read speeds than RAID 1, but this will depend on the RAID controller.
RAID 1 & RAID 0 Combinations
The combination of the RAIDs can be a great way to store data. There are two possible outcomes when you combine the two RAIDs: RAID 01 or RAID 10. RAID 10 is more popular as it uses a superior method and has the same number of drives. Both RAID 01 and RAID 10 perform the same. However, RAID 10 has higher fault tolerance.
RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0) is a configuration that combines disk striping with mirroring to protect your data. This requires at least four drives to function. However, it strips across mirror pairs. As long as one disk in each pair remains functional, you can retrieve your data.
RAID 10 improves performance and data redundancy. This is a popular choice, as it has low downtime and high write speed and read speed. However, the four-disk minimum can be costly and may not be an affordable option for many consumers.
Software or Hardware?
Software RAID
Steadfast’s dedicated servers include software RAID as an option. Software RAID 1 is included in all Steadfast servers at no additional cost. This is especially useful if you are using local storage. It is strongly recommended that all drives in a RAID array are the same size and type.
Software-based RAID can make use of some of the system’s computing power to manage the RAID configuration. A hardware-based RAID card is best when standard HDDs are used. This will allow you to optimize the system’s performance.
Hardware RAID
A dedicated controller must be installed on the server for hardware-based RAID. The engineers at Steadfast will gladly make recommendations based on your RAID configuration. Hardware-based RAID cards manage the RAID array(s) and provide logical disks to your system without any overheard.
Hardware RAID can provide multiple types of RAID configurations to the system simultaneously. This includes a RAID 1 array to boot and the application drive and a RAID-5 array to store large amounts of data.
FAQs
Is RAID 0 faster than a separate drive?
Both the drives can be read and written simultaneously. Hardware-RAID0 is faster than one drive. However, if one drive fails, then all data on both drives is lost.
Can you use RAID 0 with two SSDs?
Yes, it is possible to use RAID 0 with two SSDs. RAID 0 is a storage option that will stripe data across two SSDs, which provides more storage space and speeds up your system. This is a good option to use if you have a lot of data to back up or a high-performance computing system where a large amount of data is being saved.
Is SSD faster than RAID 0?
SSD is slower than RAID 0 in general, but in some instances, it may be faster. RAID 0 has been shown to be faster than SSD when the data is written in one large burst. The burst-writing speeds are comparable to when both are set to write in one large chunk, but the SSD will have much better reading speeds when accessing scattered data.
Conclusion
RAID 0 and RAID 1 are two different types of data storage options used by data centers. RAID 0 has the potential to offer better performance than RAID 1, however, RAID 1 offers greater protection against data loss because it’s not reliant on another system to store the data.
Essentially, if speed is your priority, RAID 0 will give you the best performance. However, if you need to ensure that all of your data is safe, RAID 1 will be the safest option.
Thanks for visiting our website www.medcpu.com! Feel free to leave a comment or question below.
Video:

Eyal Ephrat serves as the co-founder and CEO of medCPU.com, where technology is making significant strides in the field of medicine. Through his experience in purchasing PC and laptop equipment and various other tech products, Eyal Ephrat contributes valuable insights to medCPU’s mission.
